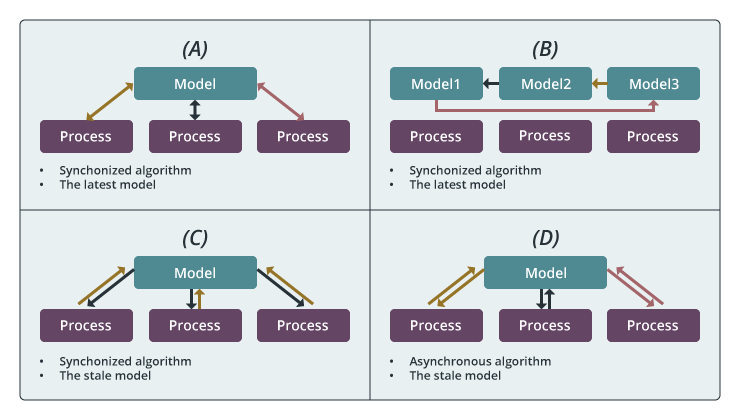
Computation Model A (Locking, use the synchronized algorithm and the latest model parameters)
This “Locking”-based computation model guarantees each worker the exclusive access to model parameters. Once a worker trains a data item, it locks the related model parameters and prevents other workers from accessing them. When the related model parameters are updated, the worker unlocks the parameters. Thus, the model parameters used in local computation is always the latest. This computation model can be implemented through Harp event-driven APIs.
Computation Model B (Rotation, use the synchronized algorithm and the latest model parameters)
The second model is a “Rotation”-based computation model that rotates model parameters between workers. Each worker first takes a part of the shared model and performs training. Then, the model is shifted between the workers. Through model rotation, each model parameters are updated by one worker at a time so that the model is consistent. This computation model can be implemented with Harp “rotate” operation.
Computation Model C (Allreduce, use the synchronized algorithm and the stale model parameters)
In this computation model, each process first fetches all the model parameters required by local computation. When the local computation is completed, modifications of the local model from all processes are gathered to update the model. This computation model can be implemented through either the “allreduce” operation for small models, the “regroup+allgather” operation or “psuh&pull” with big models.
Computation Model D (No-sync, use the asynchronous algorithm and the stale model parameters)
For the last computation model, each process independently fetches related model parameters, performs local computation, and returns model modifications. Unlike the “Locking”-based computation model, workers are allowed to fetch or update the same model parameters in parallel. In contrast to the “Rotation” and the “Allreduce” computation models, there is no synchronization barrier. This computation model can be implemented through Harp event-driven APIs.