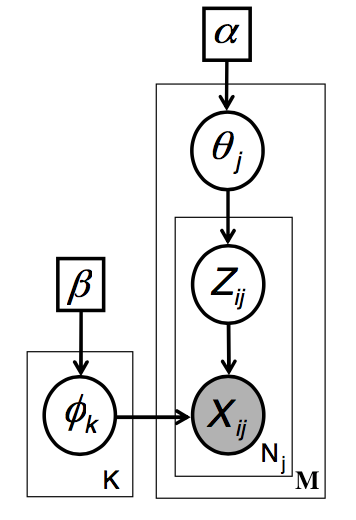
Understanding CGS LDA algorithm
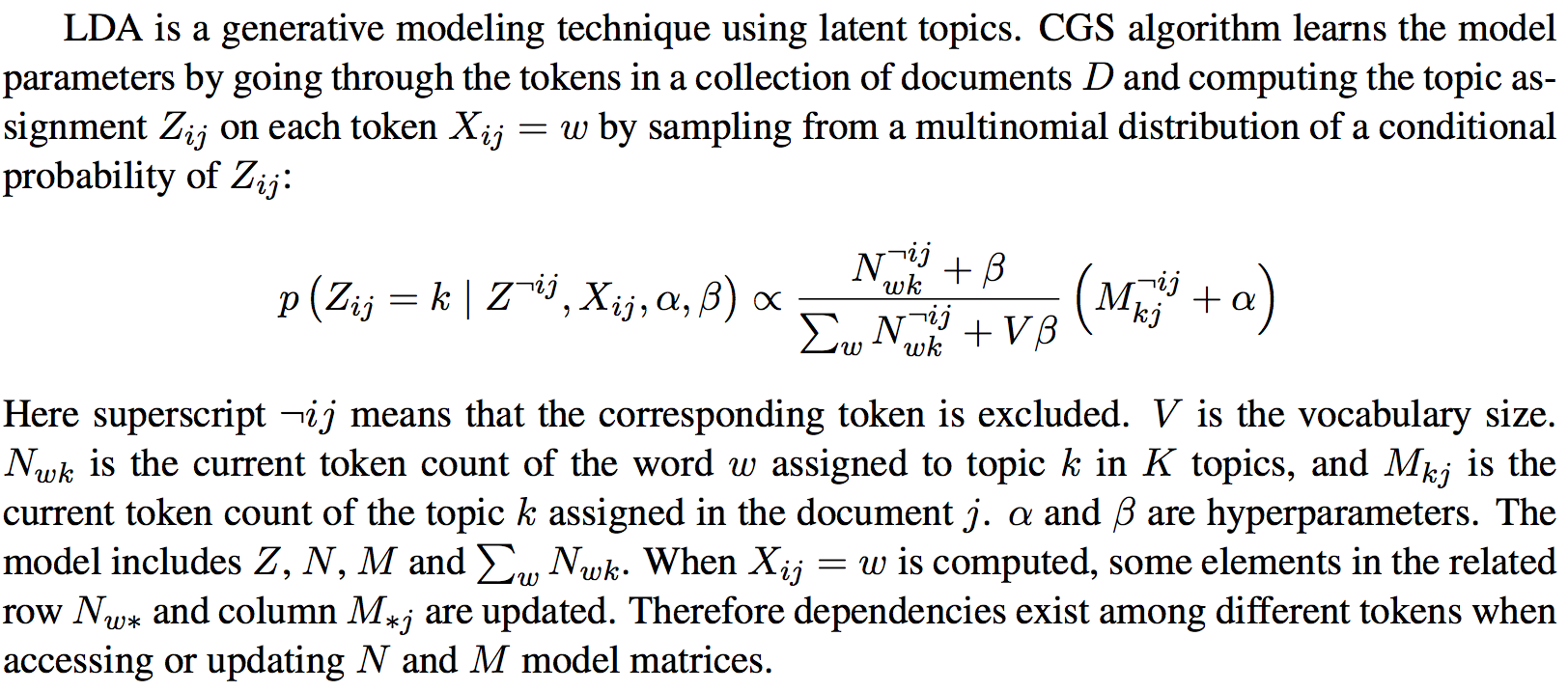
Pseudo code for CGS LDA algorithm:
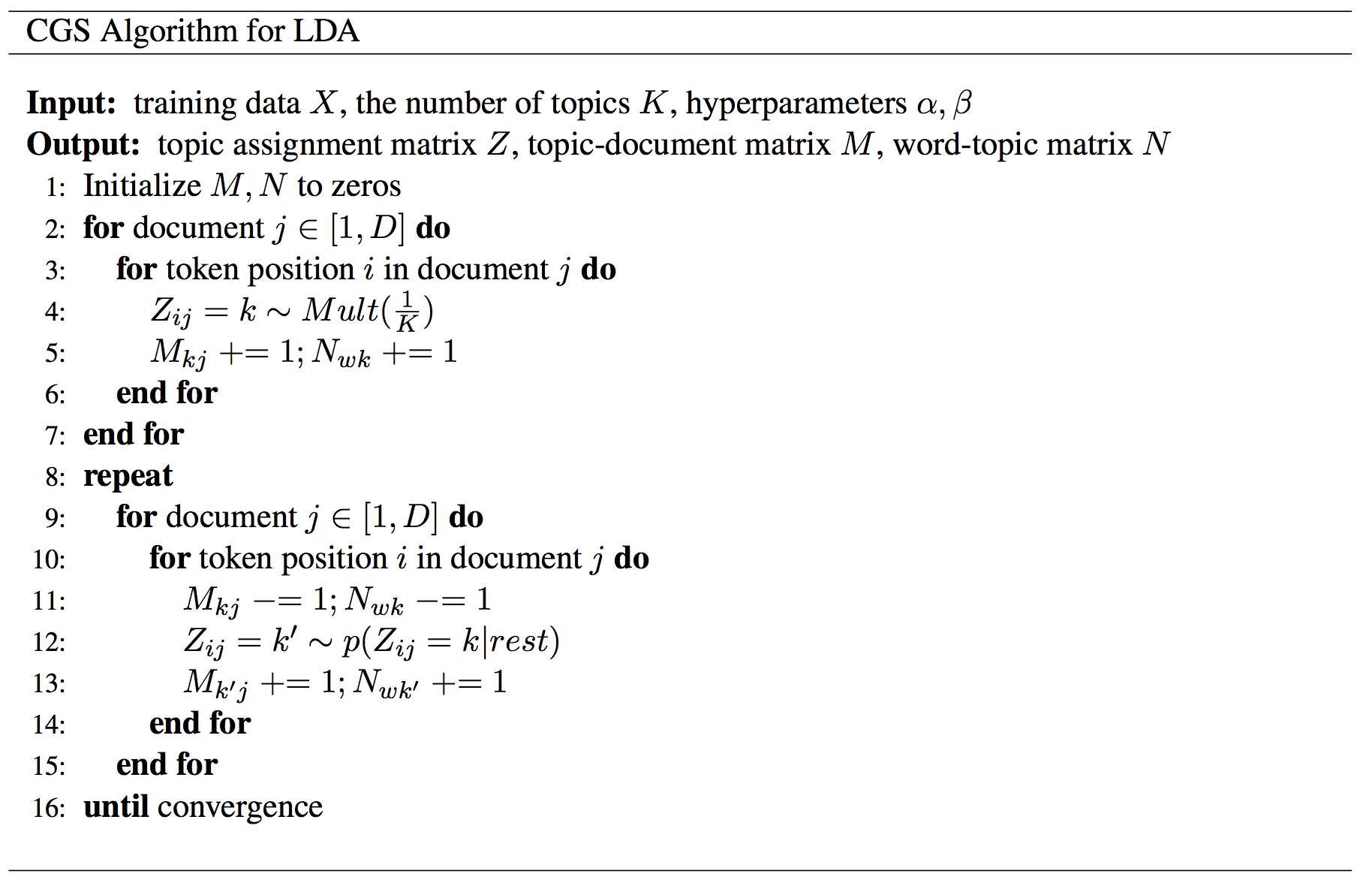
Using Model Rotation to parallel LDA algorithm
Model rotation is expressed as a collective communication. The operation takes the model part owned by a process and performs the rotation. By default, the operation sends the model partitions to the next neighbor and receives the model partitions from the last neighbor in a predefined ring topology of workers. An advanced option is that the ring topology can be dynamically defined before performing the model rotation. Thus programming model rotation requires just one API. For local computations inside each worker, they are simply programmed through an interface of “schedule-update”. A scheduler employs a user-defined function to maintain a dynamic order of model parameter updates and to avoid the update conflict. Since the local computation only needs to process the model obtained during the rotation without considering the parallel model updates from other workers, the code of a parallel machine learning algorithm can be modularized as a process of performing computation and rotating model partitions.
We adopt Model Rotation to parallel CGS LDA algorithm. The data flow and algorithm are show as follows:
Performance
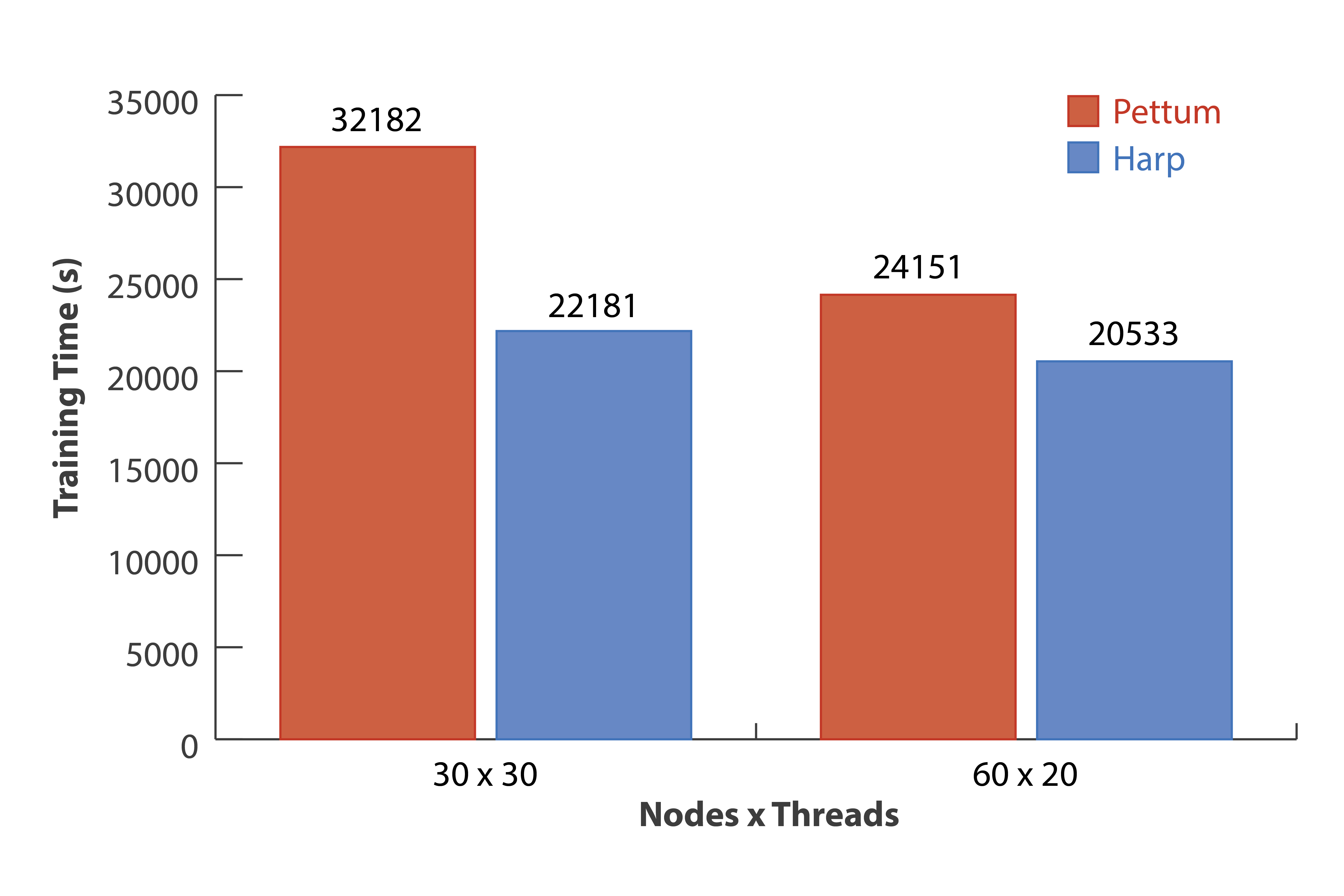
Experiments are conducted on a 128-node Intel Haswell cluster at Indiana University. Among the 32 of the nodes, each have two 18-core Xeon E5-2699 v3 processors (36 cores in total), and 96 nodes each have two 12-core Xeon E5- 2670 v3 processors (24 cores in total). All the nodes have 128 GB memory and are connected by QDR InfiniBand. For our tests, JVM memory is set to “-Xmx120000m -Xms120000m”, and IPoIB is used for communication.
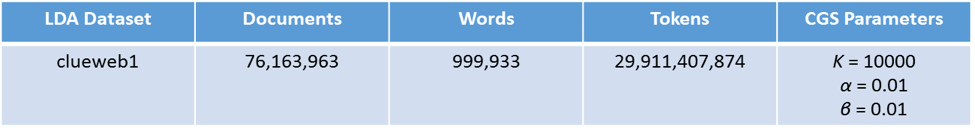
We use one big dataset which is generated from “ClueWeb09” to test LDA both on Harp and Petuum.
Through examining the model likelihood achieved by the training time, the results show that Harp consistently outperforms Petuum. We test Harp CGS and Petuum on “clueweb1” with 30 nodes × 30 threads and 60 nodes × 20 threads two configurations. Both results show that Harp CGS converges faster than Petuum. Concerning the convergence speed on the same dataset with different configurations, we observe that the fewer the number of cores used and the more computation per core, the faster Harp runs compare to Petuum. When the scale goes up, the difference of the convergence speed reduces. With 30 nodes × 30 threads Xeon E5-2699 v3 nodes, Harp is 45% faster than Petuum while with 60 nodes × 20 threads Xeon E5-2670 v3 nodes, Harp is 18% faster than Petuum when the model likelihood converges to −1.37 × 10^11.
Run LDA example
Data
You can download public data and transfer to the data format required by sgd and ccd application. Here are some datasets for your reference.
Data Format
The format for the data should be a list of doc-name wordid1 wordid2 ...>. For example,
doc1 63 264 374 4695 5441 1200 1200 25529 1707
doc2 545 1939 206863 773279 773279
...
Usage
hadoop jar harp-java-0.1.0.jar edu.iu.lda.LDALauncher <doc dir> <num of topics> <alpha> <beta> <num of iterations> <min training percentage> <max training percentage> <num of mappers> <num of threads per worker> <schedule ratio> <memory (MB)> <work dir> <print model>
<doc dir> ; input directory
<num of topics> ; K
<alpha> <beta> ; suggested setting as alpha = 50/K, beta = 0.01
<num of iterations> ; iteration number
<min training percentage> ; set the min/max training percentage to utilize timer control of synchronization
<max training percentage> ; 100,100 will set timer off, 40, 90 will works fine with timer on
<num of mappers> ;
<num of threads per worker> ;
<schedule ratio> ; blocks partition ratio for dynamic scheduler, 2 means spliting to 2xThread# X 2xMapper# blocks
<memory (MB)> ; memory setting for JVM
<work dir> ; working directory, model saved in this directory
<print model> ; True/False, save model W if set to Ture
Example
#put data onto hdfs
cp $HARP_ROOT_DIR/datasets/tutorial/nytimes-30k/nytimes-30K.mrlda .
mkdir data
cd data/
split -l 1000 $HARP_ROOT_DIR/datasets/tutorial/nytimes-30k/nytimes-30K.mrlda
cd ..
hadoop fs -mkdir -p /harp-test/cgs/
hadoop fs -put data /harp-test/cgs/
#run lda training
hadoop jar harp-java-0.1.0.jar edu.iu.lda.LDALauncher /harp-test/cgs/data 100 0.5 0.01 100 100 100 10 16 2 10000 /harp-test/cgsout True