Before going through this tutorial take a look at the overview section.
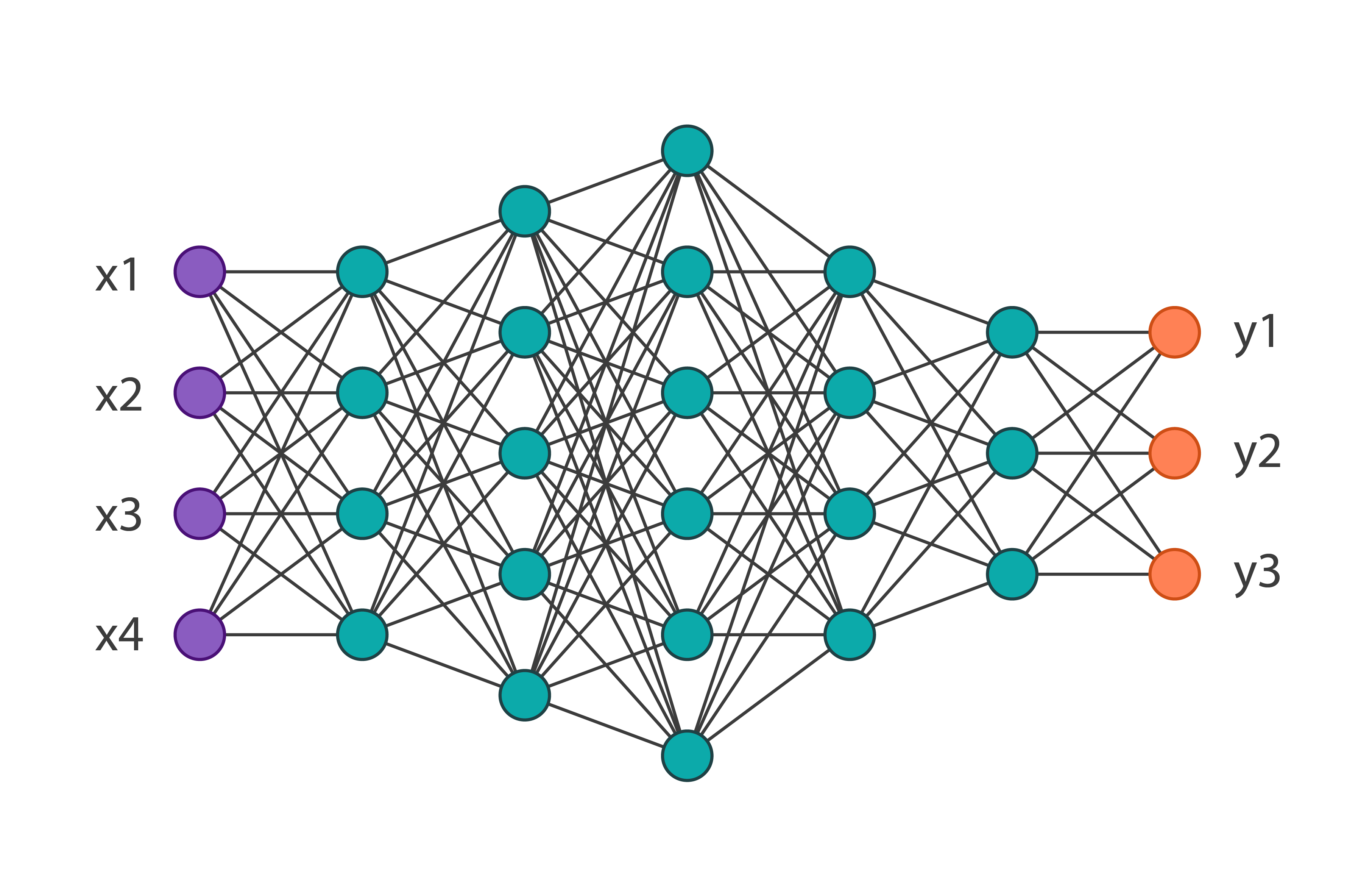
Neural networks are a set of algorithms, which is based on a large of neural units. Each neural unit is connected with many others, and forms a network structure. Computation happens in the neural unit, which combines all the inputs with a set of coefficients, or weights, and gives an output by an activation function. A layer is a group of neural units, that each layer’s output is the subsequent layer’s input. A learning algorithm tries to learn the weights from data, and then the network can be used to recognize patterns.
Here, we give a simple tutorial on how to parallel a standard implementation of the BP algorithm for a feed-forward network.
PARALLEL DESIGN
What is the model? What kind of data structure is applicable?
Weights matrices, including the biases for each node, between each adjacent layers are the model in neural network. It is a vector of double matrix.
What are the characteristics of the data dependency in model update computation? Can updates run concurrently?
In the core model update computation in BP training algorithm, each data point, or a minibatch, should access all the model, compute gradients and update model layer by layer from the output layer back to the input layer.
The nodes in the same layer can be updated in parallel without conflicts, but there are dependency between the layers. But generally, it is not easy to utilize these network structure related parallelism.
Which kind of parallelism scheme is suitable, data parallelism or model parallelism?
Data parallelism can be used, i.e., calculating different data points in parallel.
No model parallelism, each node get one replica of the whole model, which updates locally in parallel, and then synchronizes and averages when local computation all finish.
which collective communication operation is suitable to synchronize the model?
Synchronize replicas of the model by allreduce is an simple solution.
DATAFLOW
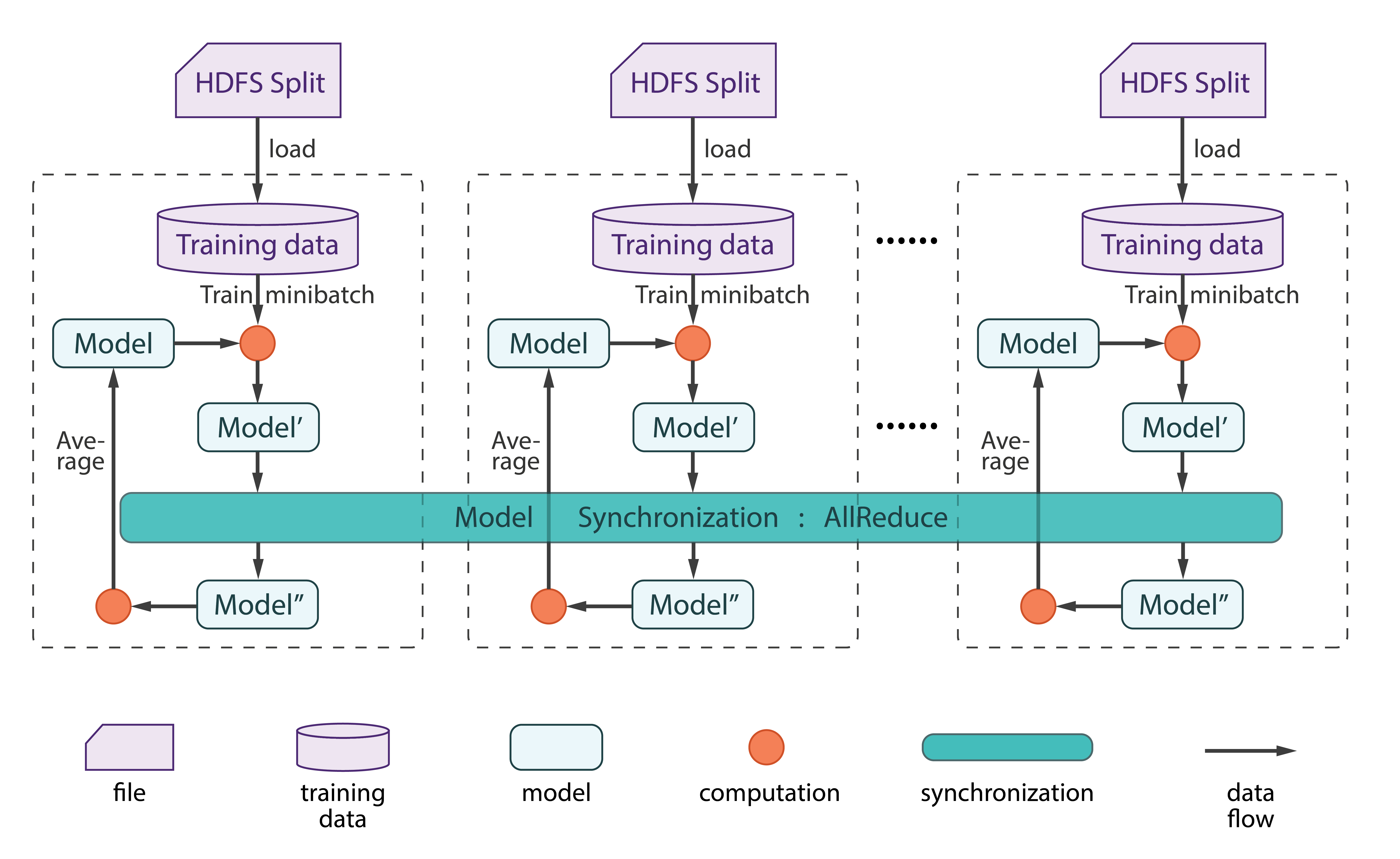
Step 1 — Set Table
The data format wrapper code is in charge of the conversion between the native DoubleMatrix and Harp Table.
public Table<DoubleArray> train(DoubleMatrix X, DoubleMatrix Y, Table<DoubleArray> localWeightTable, int mini_epochs, int numMapTasks, double lambda) throws IOException
{
Vector<DoubleMatrix> weightMatrix = reshapeTableToList(localWeightTable);
setTheta(weightMatrix);
trainBP(X, Y, lambda, mini_epochs, true);
Table<DoubleArray> newWeightTable = reshapeListToTable(this.getTheta());
return newWeightTable;
}
Step 2 —Communication
The code snippet for the core part of computation in the iterative training. There are only a few lines of differences between the harp distributed version and the original sequential version.
// Calculate the new weights
// argument data type conversion and call the train() in the underlie library
weightTable = localNN.train(X, Y, weightTable, n, numMapTasks, lambda);
// reduce and broadcast
allreduce("main", "allreduce" + i, weightTable);
// Average the weight table by the numMapTasks
weightTable = localNN.modelAveraging(weightTable, numMapTasks);
DATA
The MNIST dataset is used in this tutorial.
Run example
Put data on hdfs
#download the dataset
python $HARP_ROOT_DIR/datasets/tutorial/mnist/fetech_mnist.py
#split into 2 parts
python $HARP_ROOT_DIR/datasets/tutorial/mnist/split_mnist.py mnist_data 2
#upload data to hadoop
hadoop fs -mkdir -p /nn/batch
hadoop fs -put mnist_data_?.* /nn/batch
Compile
Select the profile related to your hadoop version. For ex: hadoop-2.6.0. Supported hadoop versions are 2.6.0, 2.7.5 and 2.9.0
cd $HARP_ROOT_DIR
mvn clean package -Phadoop-2.6.0
cd $HARP_ROOT_DIR/contrib/target
cp contrib-0.1.0.jar $HADOOP_HOME
cp $HARP_ROOT_DIR/third_parity/jblas-1.2.4.jar $HADOOP_HOME/share/hadoop/mapreduce
cp $HARP_ROOT_DIR/third_parity/neuralNet-1.0.0-SNAPSHOT.jar $HADOOP_HOME/share/hadoop/mapreduce
cd $HADOOP_HOME
Run
hadoop jar contrib-0.1.0.jar edu.iu.NN.NNMapCollective
Usage: NNMapCollective <number of map tasks> <epochs> <syncIterNum> <hiddenLayers> <minibatchsize> <lambda> <workDir>
Example
hadoop jar contrib-0.1.0.jar edu.iu.NN.NNMapCollective 2 20 5 100,32 2000 0 /nn
This command run harp neuralnetwork training on the input dataset under /nn, with 2 mappers. Training process goes through 20 times of the training dataset, averages the model every 5 iteration for each minibatch. The minibatch size is 2000, lambda is default value 0.689. There are 2 hidden layers, with 100 and 32 nodes each. Finally, it outputs the accuracy on the training set into the hadoop log.